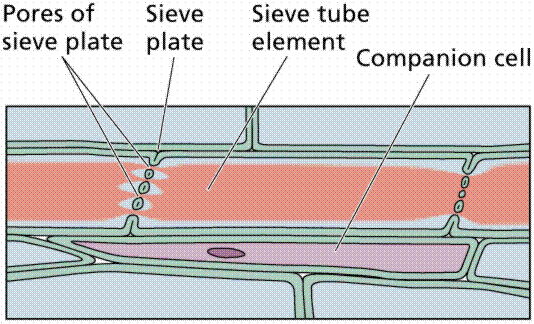
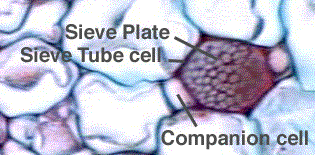
Phloem
The plant cells that transfer the food materials from the leaves to the other parts of the plant are called as Phloem cells. The phloem is usually present nearer the xylem and comprises of two cell types known as sieve cells and companion cells. The sieve cell is elongated and form part of sieve tube. They are made up of sclerenchyma cells. The sieve cells do not possess nuclei while the companion cells will possess nuclei. Companion cells are arranged around the sieve tubes. The sieve tubes are helpful in transporting the sugars and other food substances from the plant leaves to the rest of the plant parts. The sieve tubes are joined with each another by sieve plates, which are porous. Phloem also constitutes parenchyma cells.
Epidermis
The epidermis is the top most layer of the plant, which helps in protecting the plant from fungal and other organismal invasions. The epidermis also helps in stopping the loss of water. Some plants have epidermis covered by a waxy cuticle. The presence of cuticle prevents further loss of water.
Guard cells
The gaseous exchange that takes place between the plant inner and outside environments is carried out in plants by stomata. The stomata are present extensively in leaves and stems. The stomata aid in exchange of gases as well as act as openings that allow even the water loss.
The guard cells are present surrounding the stomata openings and they are of bean shaped. Stomata are usually considered beneficial in the exchange of carbon-di-oxide, oxygen and water-vapour into the atmosphere.
No comments:
Post a Comment