Plants are eukaryotic organisms and the plant cell has many organelles similar to those present in animal cell except few as dissimilar. The plant cells do not possess centrioles and intermediate filaments. Intermediate filaments constitute keratins, neuro-filaments, nuclear lamins and vimentins. Plant cell is unique with the presence of large vacuoles, cell wall and plastids. The other organelles present in the plant cell, which resemble those present in the animal cell are microtubules, ribosomes, peroxisomes, nucleolus, mitochondria, nucleus, ER, plasma membrane and Golgi apparatus.
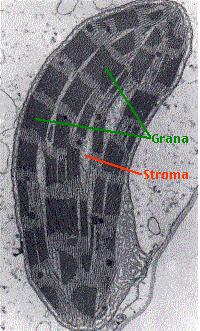
Plastids are organelles with pigment and chloroplasts are one type of plastid. Chloroplasts usually appear as disk shaped. They have the diameter of five to eight micrometers and the thickness of chloroplasts is in the range of two to four micrometers. Plant cells typically contain about 20 to 50 chloroplasts. The chloroplasts have three types of membranes such as inner and outer membranes and also thylakoid membrane.
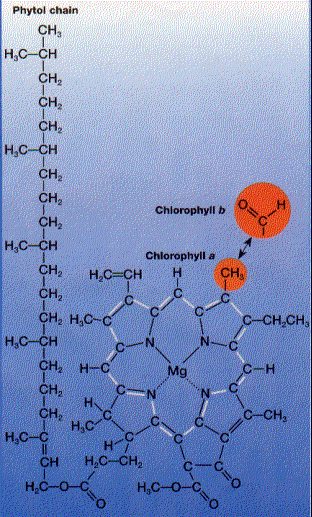
Chloroplasts consist of chlorophyll molecules, which are responsible for the green color of the chloroplasts. The chlorophyll pigment will receive the sunlight energy and transfer the energy in the desired form for carrying out photosynthesis. The plants possess two types of chlorophylls called chlorophyll a and b. The other pigments present in the chloroplasts are carotenoids, which are red to yellow in color.
The plant cell wall is made up of cellulose fibrils, which are gathered along with other types of polymers like lignin and pectin. The stiffness of the fibers is determined by the linear shaped cellulose molecules forming intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
The cell walls of parenchyma cells and other meristematic cells have common thickness. The cell wall here is called as primary cell wall. The plasmodesmata are connected to the adjacent cell through the primary cell wall. The secondary cell wall is known to provide strength to the cells and tissues. Secondary cell walls are observed to be present in the cells such as collenchyma, sclerenchyma and xylem. The secondary wall is an extra deposition of lignified cellulose.
Plants have large vacuoles and they are surrounded by just one membrane. The major functions of vacuoles are storing the malic acid in CAM plants, wastes, and foods as well as in the maintenance of cell turgor. The plant cell will protect itself from bursting when it is placed in a hypotonic solution due to the presence of cell wall.
If the plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution or in the sea water, the cell loses water and might wilt. The shrinking of cell makes the plasma membrane to move away from the cell wall.
No comments:
Post a Comment